Acute Renal Failure
What is AKI?
According to The Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO), which it the most current and preferred definition, it is:
an increase in serum creatinine of ≥0.3 mg/dL within 48 hours OR an increase in serum creatinine of ≥50% within 7 days OR Urine output of <0.5 mL/kg/hour for >6 hours
Etiology:
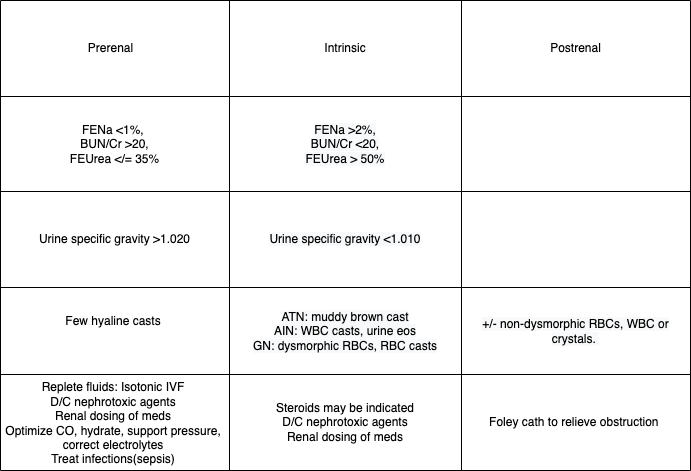
1)Prerenal: Decreased renal perfusion (70% of causes)
a. Intravascular volume depletion: Dehydration, third-spacing
b. Decreased arterial pressure: CHF, sepsis,
c. Extracellular fluid loss : Burns, diarrhea, vomiting, diuretics or hemorrhage
d. Decreased CO: CHF, shock
e. Medication changes to renal vasculature: ACE-i, ARBs, NSAIDs, Tacrolimus, Cyclosporine
2)Intrinsic: classified according to the site of injury
a. Vascular Injury: afferent arteriolar vasoconstriction --> decreased GFR (Ex. TTP, Vasculitis, RAS, malignant HTN)
b. Glomerulonephritis: Includes renal (PSGN, IgA, membranoproliferative GN), hematologic dz (HUS, TTP), systemic inflammation (SLE, HSP), and pulm-renal syndromes (Goodpasture, granulomatosis with polyangitis). +hematuria( RBC casts) and proteinuria.
c. Interstitial Nephritis: analogous to an allergic rxn in the kidney, may be associated with fever, arthralgia, and rash. Allergic rxns can be due to drugs (penicillin, cephalosporin, NSAIDs, Sulfas, PPIs), autoimmune disorders (ex. SLE), infections (diphtheria, GAS), or other dzs such as sarcoidosis.
d. Acute Tubular Necrosis (ATN): cell death and necrosis from renal ischemia (prolonged hypoperfusion aka prolonged prerenal state), toxins( rhabdo, uric acid crystals, radiocontrast dye, hemolysis, amioglycosides)
3)Postrenal: Renal outflow obstruction
a. Intrarenal/tubular: crystals, nephrolithiasis
b. Ureteral: bilateral nephrolithiasis, thrombosis, edema from retrograde pyelography
c. Extra-ureteral: Bladder or cervical CA
d. Bladder neck: neurogenic bladder, autonomic neuropathy
e. Urethra: BPH, prostate CA, urethral stricture
-Evaluate for volume status, skin tenting LE edema, ascites, skin rash, purpura, bladder distension, prostate enlargement etc.
-Monitor urine output, sediment, UA, electrolytes
-Calculate FENa (collect urine sample prior to IV fluid or diuretic tx). If patient is on diuretics utilize FEUrea.
-FENa: (Una/Pna)/(Ucr/Pcr), FEUrea: (Uurea/Purea)/(Ucr/Pcr)
- Renal US to r/o obstruction or assess for hydronephrosis
-Serology for complement levels and renal biopsy if etiology is unclear.
Please comment on workup, complications, and therapies
No comments to display
No comments to display