Hypernatremia
Definition:
- Serum Na >135 mmol/L. Chronic means > 48 hours. Acute means < 48hrs.
Etiology:
Renal water loss (U osm <700-800)
- loop diuretics
- Osmotic diuresis (hyperglycemia, mannitol, urea)
- Diabetes Insipidus: Central (trauma/post-surgical, pituitary lesions, sheehan's syndrome) vs Nephrogenic (congenital, sickle cell, hypercalcemia, severe hypokalemia, drugs: lithium, amphotericin)
Extra-renal water loss (U osm >700-800)
- GI loss: vomiting, NGT, osmotic diarrhea, lactulose, malabsoption
- Insensible loss: fever, burns, exercise
- hypertonic intake: hypertonic saline, excess salt intake, hypertonic sodium bicarb pushes
Evaluation: U osm, U Na, volume status
- Causes is often apparent from history and review of medications, nutrition, and intake/output
- Determine if there is inappropriate renal free water loss
- In DI, urine will be inappropriately dilute (<300 mOsm/L). Water deprivation test will result in rising serum Na and persistently dilute urine. Desmopression response after deprivation can differentiate nephrogenic (no response) vs central (concentrated urine)
Management
Step 1: calculate free water deficit. Can also use MD Calc
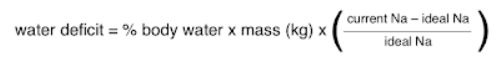
- % body water for 0.6 for male and 0.5 for female. If elderly use 0.5 for male and 0.45 for female
- Give free water deficit enterally
- Do not forget to correct Na if hyperglycemia also present
Step 2: Rate of correction
- Divide free water deficit by 24hrs and give accordingly. Check serum Na every 6-12hrs to adjust correction rate and follow urine output
- Rate of correction depends on acuity of onset and risk:
- chronic (>48hrs): 12 mEq/d appears safe w/o risk of cerebral edema
- acute (<48hrs): may decrease Na by 2 mEq/L/h until Na 145
- hyperacute (min-hrs) & life threatening (ICH, seizure): rapidly infuse D5W plus minus emergent HD
Diagnosis and Management of Disorders of Body Tonicity-Hyponatremia and Hypernatremia
Rate of correcting of hypernatremia
No comments to display
No comments to display